Go Shop: Google Shopping The full guide
- Paid Campaigns
- June 1, 2020
How do you create a catalouge? How do you build a store? and what to watch out from? All the necessary steps on your way to a google store
It is no secret that Google has changed from a search engine to an online shopping empire in recent years. The concept was simple: connect businesses with net surfers where everyone’s already searching – Google. Despite the tempting platform, Google Shopping requires skill and knowledge. Not to worry, that’s what we’re here for, to give you a complete and updated guide on building a Google Shopping campaign that will give you the best outcomes, with all the changes, updates and improvements made over the last couple of years.
» Check out our Blog for more digital marketing news
» Need some help with paid campaigns?
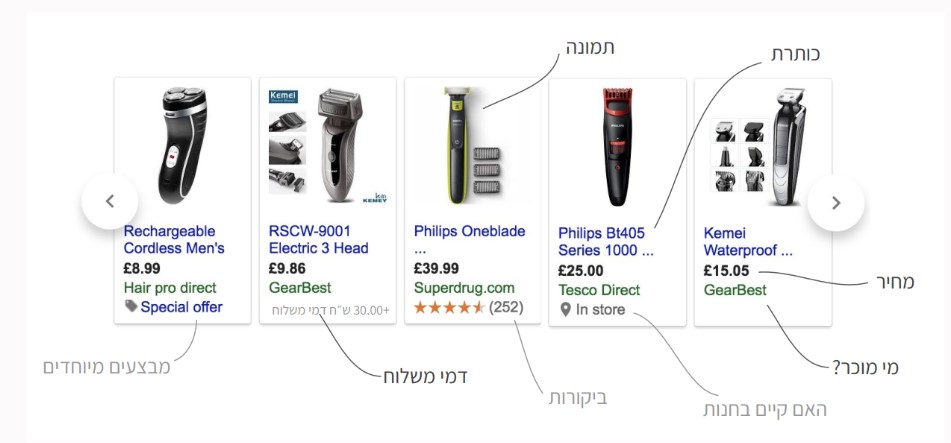
What are Google Shopping ads?
» A Shopping ad includes a photo, headline and price; with a convenient-to-use display and appeal for purchasing.
» Shopping ads appear in Google search results pages and are displayed differently than Search ads (we will later detail the advantages of Shopping ads compared to Search ads).
» It is important to know that Shopping-type campaigns are approved only for advertisers who have an E-Commerce website (trading sites) which sell physical products, and as of now there is no option to publish any services (insurance, courses, etc.).
A Shopping campaign has a higher conversion rate than a Search campaign. The difference derives from several factors:
1. Shopping campaigns can present the product’s picture and (updated!) price, unlike a Search ad, where you cannot display a picture and an updated price is hard to show (especially when the prices change often).
2. The Shopping campaign’s higher conversion rate shows that it is positioned in the Action stage of the panel, as opposed to a Search campaign which is located more in the Consideration stage. Furthermore, a Shopping campaign click-rate is usually cheaper than in Search campaigns.
What does a Google Shopping ad look like?

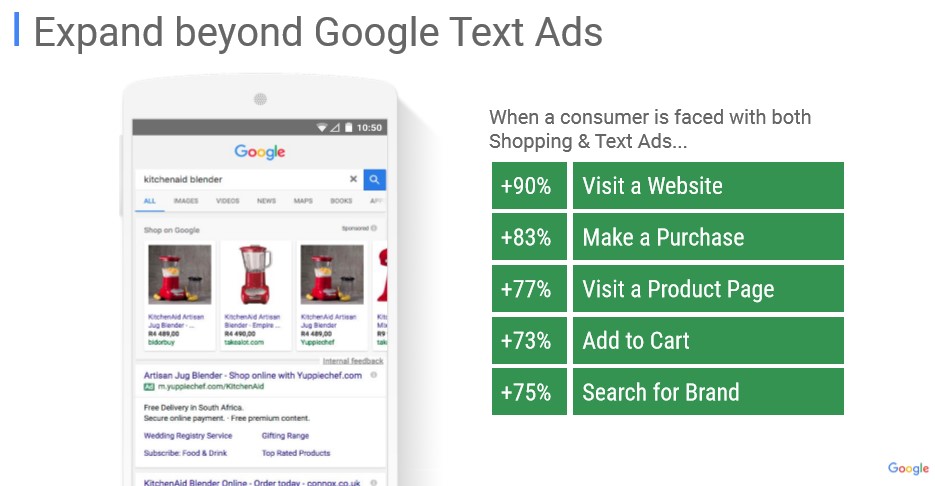
Notice that when a Google Shopping ad shows up along with a Search ad, there is another advantage: when a user searches Google for a specific product and comes across both Shopping and Search ads (SERP – Search English Result Page), the chances of entering the site and purchasing the product increases by 90% and 83% respectively – meaning it takes up more space for your product on Google search results.

Shall we get to work?
Stage 1 – Understanding the logic and campaign structure:
The most critical stage of the campaign is actually “laying the groundwork”. Before we start establishing it, we have to make a decision regarding the products’ hierarchical order in the catalogue, so we can provide the system with as much information about each product as possible. This way, we will get better control of the products and can perform efficient and performance-based automation per product/product groups (depending on the hierarchy we choose).
So how do we begin?
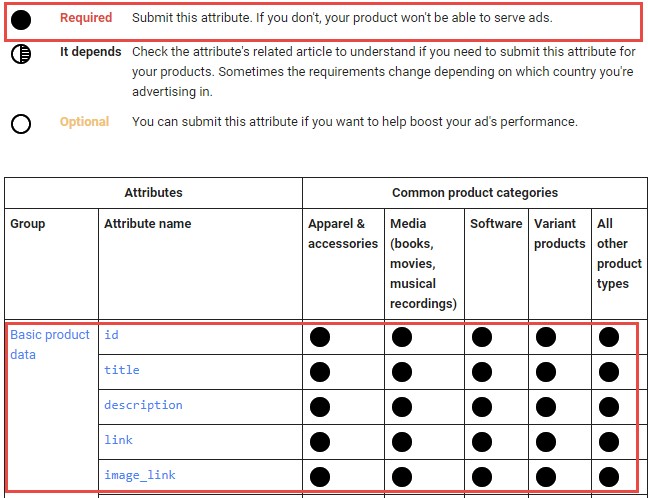
It all starts with making a catalogue. A ‘catalogue’ is a table (mostly an Excel sheet) made out of a list of products, with each having different attribute columns. We will link the catalogue to the Merchant Center (Google’s virtual store) and link the Merchant Center to the Google Ads account. Google Ads will recognize the different products in the catalogue, and we can start setting up the Shopping campaign!
How to build a catalogue?
Building a good and organized catalogue is key to your Shopping campaign’s success. That is why the data should first be sorted meticulously and according to Google’s specific instructions:
After filling out the catalogue according to Google’s instructions, we must notice the following significant emphases:
Building a headline:
The headline is the most important part of a good Shopping campaign, it is important to put a lot of thought into building it the right way, so that it contains as much information for the user as possible.
There are different and varied verticals, each with different headline suggestions. We have gathered a few examples of leading verticals; however, if you come across a new vertical, exercise thought and logic when building the headline. Note, it is important to remember that while the headline can contain up to 150 characters, the displayed headline will be partial, and users will only be able to see the entire headline if they scroll it with their mouse. That is why it is important to mention the most important parts of the headline in its beginning (the first 70 characters).
From Google’s instructions we learn that each product contains the most important information in the headline, so users can decide if it is relevant for them based on the photo, the price and headline alone. Only after they show interest and click the ad will they be exposed to additional information, such as the product’s description:
Building a product description:
The product description can contain up to 1,500 characters, which Google scans along with our product headline, to identify the product’s content and target relevant expressions accordingly. That is why it is very important for the description to contain as many key expressions as possible which would contain Google search volumes:
Google_Product_Category:
Despite Google presenting the above category as “optional”, in our experience with many campaigns of this kind, we have found that this category is critical for the success of the campaign and is another significant level in Google’s process of understanding your product. To make sure that the product details you are sending meet the high-quality criteria, mind the next few highlights:
» Use only the categories Google has predefined. You can choose to send the identifier or the full product description pathway. Here is a link where you can find all the existing categories.
» It is recommended to use the category which best describes your product. Choose the category according to the main function of the product. For instance, if an MP3 player has other uses (for example, a clock) its main use is still as an MP3 player which is why the category best suited to it would be Electronics > Audio > Audio Players & Recorders > MP3 Players (233).
» It is recommended to be as specific with categories as possible. For instance, for an MP3 player charger, you should use the MP3 Players Accessories category.
» In case you are using a text, it is important to make sure to copy it exactly as it appears in the file. The same goes for the number, if you choose to use a number make sure you use the exact same number.
Customer Ranking
This category is also not defined as required by Google but will help you improve the ads’ performance and get more conversions out of them.
Customer Ranking is a kind of automatic add-on which accentuates advertisers with high rankings. The role of consumer rankings shown under the ads is to help the user find businesses which offer quality services and products.
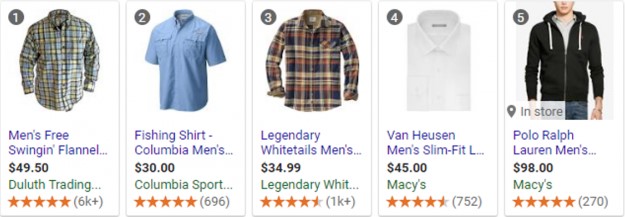
What does it look like? Consumer rankings include the following data:
» An out-of-5 stars rating.
» The number of reviews the business has (in parenthesis).
» A standout feature (for instance, average delivery time) which represents the main reason the business received this ranking (in case such data is available):
Where do those rankings come from? Google bases its consumer rankings on a few sources:
» Google Consumer Reviews – a free program you can register to on your Merchant account, which gathers reviews from customers who purchased a product at the site.
» Accumulated performance in shopping research initiated by Google – Google might also use this shopping research to set some of the definitions used for ranking the business.
» Rankings from third-party sites – many E-Commerce sites use third-party sites to gather reviews and you could add all that gathered data to your Merchant account, presenting the ranking and reviews along with the Shopping ads.
Images
It is important to use good-quality images (recommended 800×800 pixels), with a white background considered the best format.
Pay attention, images with text or a logo on them are prohibited. In addition, it is important to make sure that only the sold product is shown, and not a set of products to which it belongs. If you are selling pants, you should only display the pants and not other products, which might confuse the user as to the offered product:


Custom Labels
Using Custom Labels options, you can add an additional hierarchy to the catalogue beyond Google’s required settings. You can use up to five parameters as you please (0-4), this is where you need to think about which parameters you would like to cross-section and add as Custom Labels.
Here’s an example of using Custom Labels:
Custom label 0 = Gender
» Custom label 1 = Category
» Custom label 2 = Model
» Custom label 3 = Product name
» Custom label 4 = Color
External catalogue management tools
We at Operad use a unique technological catalogue management system which allows us to perform the following actions:
» Manipulating the catalogue without making changes to the site and/or using a programmer, building headlines comprised of several catalogue columns (brand, product, color, etc.), changing values in certain columns and more.
» Adding columns to the catalogue.
» A/B Testing for various catalogue checks.
» Adding automatic rolls to update the catalogue, in case it is needed.
Stage 2 – Opening a Merchant Center account and uploading the catalogue
The Merchant Center’s role in this activity is actually to serve as a type of bouncer for Google. And so, when we upload the catalogue to the Merchant Center, Google reviews the products in our catalogue and makes sure they match its requirements and policies.
Diagnostics – This is what the diagnostics dashboard looks like:
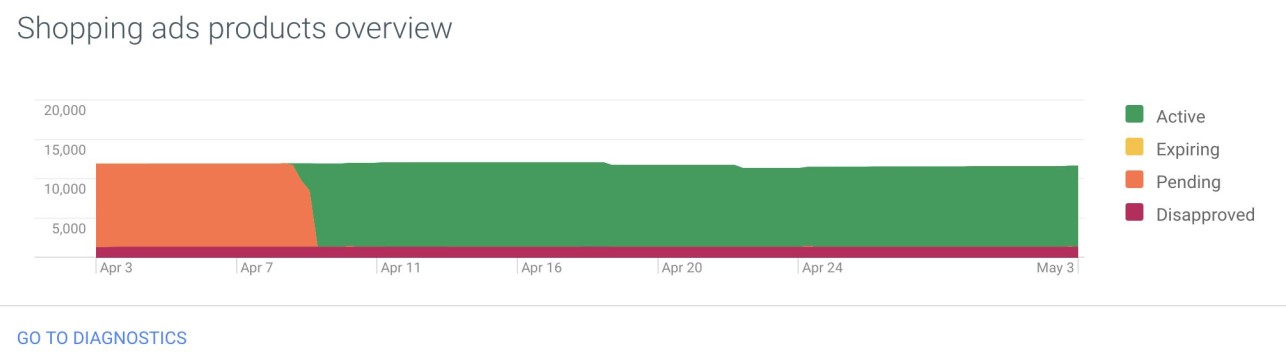
After uploading the catalogue, you can see details about products with various issues in the diagnostics window, products which were not authorized to be uploaded or optimization recommendations, and dealing with issues arising during the test.
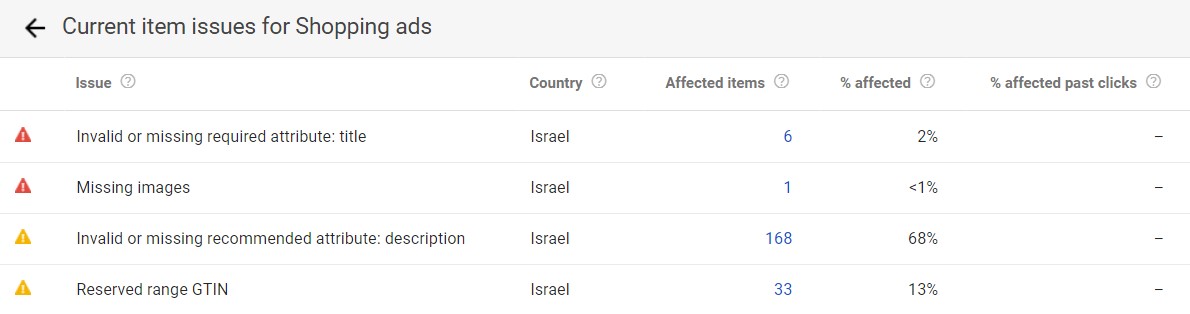

There are three types of possible issues in the diagnostics window:
» Errors – usually pointing to the account’s suspension or items that were unauthorized due to fundamental issues preventing them from being displayed to users. In short, everything that defies Google’s required instructions.
» Missing Images –quite simple, just as a display window cannot remain empty there must be an image of the relevant product.
» b – the item can be approved, but with outstanding issues that might have a negative impact on the ads’ performance, so much so that it might lead to the items or even the entire account being suspended.
» A barcode (GTIN) which leads to more than one product, causing duality in the system.
» Alerts – even though an item might be approved without any warning, Google will display optimization suggestions for the product data, aiming at improving data quality. For instance:
» Long Titles – an item title that is too long. Unlike text messages in Google Ads, the ad will be approved but the text will be cut off in the middle as the product is displayed, and we do not want that. This should be resolved before the upload, while taking advantage of the text area wisely.
After the products are authorized, we can start building the campaigns themselves; it is important to perform an Account Link between Merchant Center and Google Ads, in order for us to have the opportunity to create Shopping-type campaigns.

Stage 3 – Smart vs. Manual
» Smart Campaigns – Smart Shopping campaigns are based on Machine Learning, and thus are able to increase the amount of sales while maintaining set costs. The algorithm knows how to identify a user’s conversion chance, matching the bid and the presented product (ad) automatically to reach the goals set. Smart campaigns incorporate some re-marketing activity in the media network for users with high conversion chances, which is why Display ads should be added to the campaign. Ads by smart campaigns can show up on the search network, the Google media network, YouTube and Gmail. To establish a smart Shopping campaign, we should add a tracking tag on the site level and a re-marketing list, consisting of at least 100 active users attached to the account. Here is an example of the performance differences while using a smart campaign compared to a regular one:
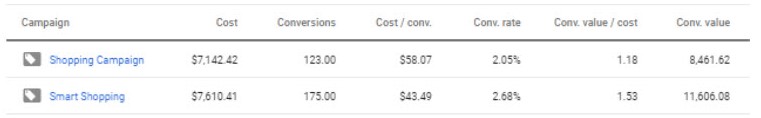
» We see a 42.28% increase in conversions, a 33.52% decrease in cost per conversion and even about 37.16% increase in profit.
» Standard Campaigns (not Smart ones) – Shopping ads are allowed to be displayed in the following places on the Web:
– In “Shopping” tags of a Google search (in select countries).
– In a Google search alongside search results (separate from text ads) and on Google Images.
– Partner sites of the Google search network (in case you have included search network partners in your campaign settings).
– On Google’s media network.
In addition, we should define bids at the product/product group level, which is why the optimization in this campaign is manual. This method does not use Machine Learning, causing it to lose the advantage of using signals the system receives about the user, adjusting the designated bid intended for that user.
Pay attention, you cannot run both a smart and standard campaign simultaneously. In this case, the system will prioritize the smart campaign over the standard one, and it will not receive any exposure.
Stage 4 – Establishing the campaign and initial settings
When choosing to start a new Shopping-type campaign, we will encounter a page where we can set the basic campaign characteristics, assuming there is a proper account link between Google Ads and Merchant Center. We will start by defining the goal of the advertisement, in this case we will choose “Sales”:


Then we will choose the Shopping option from the campaign types:

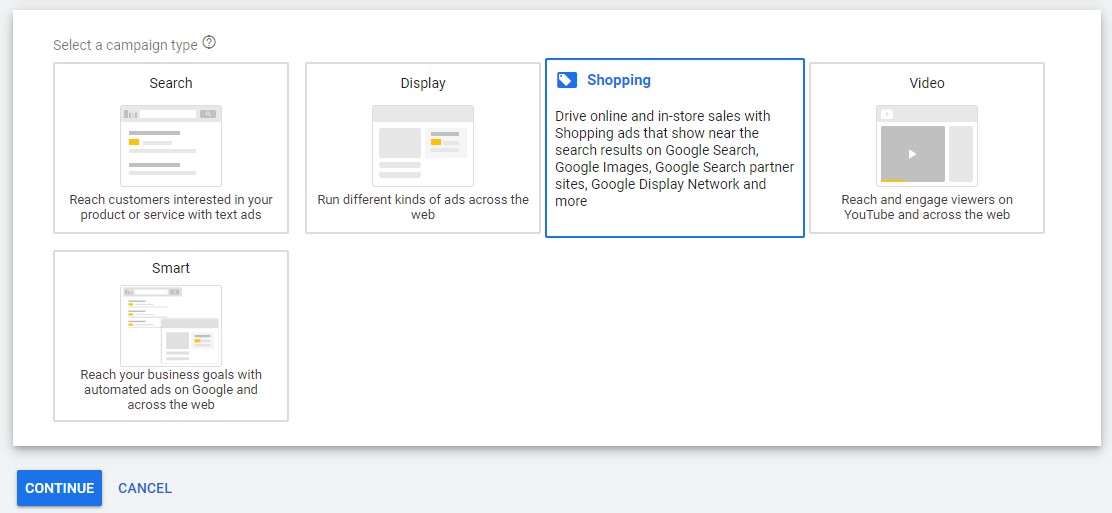
We will make sure the Merchant account is linked and choose the country in which we wish to sell our products.
* Pay attention, you have to specifically define which countries you would like to display your ads in, since the Google Ads display options are vast and also include an option to advertise in a wide range of countries and languages; it is possible that your campaign will be available to display in other countries which speak the same language or use the same currency. Meaning, if you are interested in selling to only one country, you should specifically target it at the appropriate location.
Stage 5 – The last stage
Finally, at this stage we can choose to run a Smart or standard campaign.

Optimizing market competition (reports on Merchant Center).
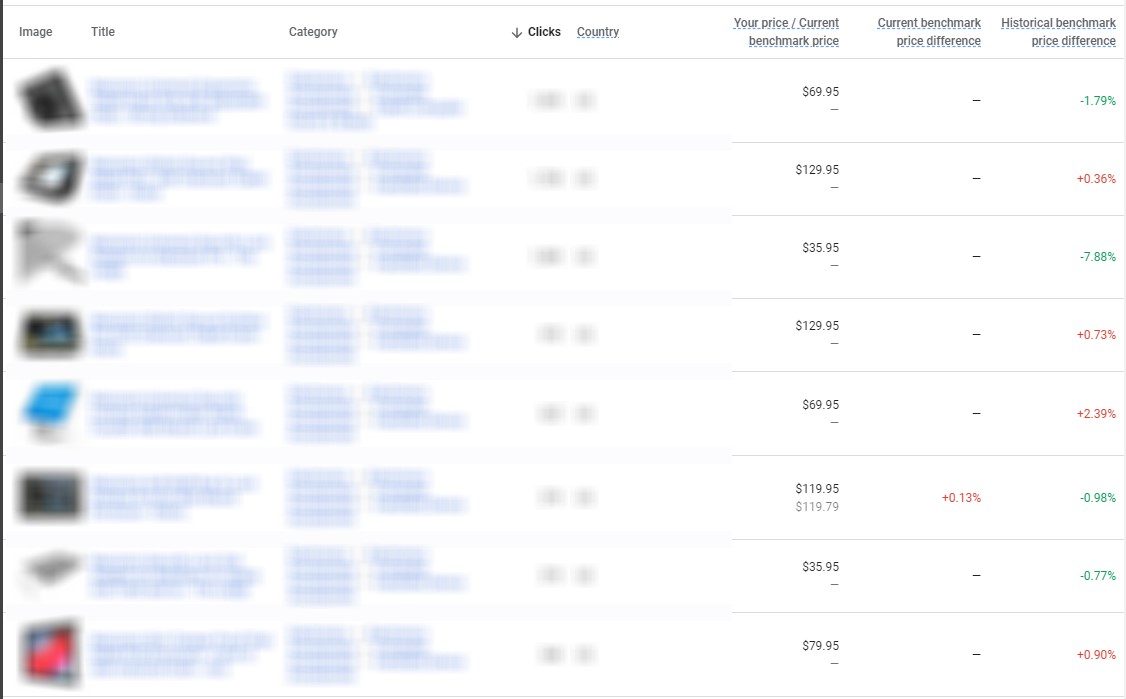
Price Competitiveness Report – displays the average price of each product by cross-sectioning our price as well as our competitors’ price.


This report helps understand how to set the price for each product. We can sort the report according to product, product type, category or brand. By sorting according to product or clicking on display products, a detailed table opens, containing all the data regarding each of the products.

To sum up
Over the past two years, retailers who were smart enough to learn the right way to use Google Shopping have already gained quality traffic that this advertising tool brings with it, in real time. Correct construction of the campaigns, making sure the smallest technical details are upheld and constantly learning the tool’s updates will guarantee that you make the most of the potential niches your business focuses on. For more information, help or managing Google Shopping activities, contact us 😊
